Hash table
const superPrimitiveHashingFunc = (string: string) => {
var hash = 0;
for (var i = 0; i < string.length; i++) {
hash += string.charCodeAt(i);
}
return hash;
};
export class HashTable {
private collection: any = {};
public add(key: any, value: any) {
const theHash = superPrimitiveHashingFunc(key);
if (!this.collection.hasOwnProperty(theHash)) {
this.collection[theHash] = {};
}
this.collection[theHash][key] = value;
}
public remove(key: any) {
const hashedObj = this.collection[superPrimitiveHashingFunc(key)];
if (hashedObj.hasOwnProperty(key)) {
delete hashedObj[key];
}
if (!Object.keys(hashedObj).length) {
delete this.collection[superPrimitiveHashingFunc(key)];
}
}
public lookup(key: any) {
var theHash = superPrimitiveHashingFunc(key);
if (this.collection.hasOwnProperty(theHash)) {
return this.collection[theHash][key];
}
return null;
}
}
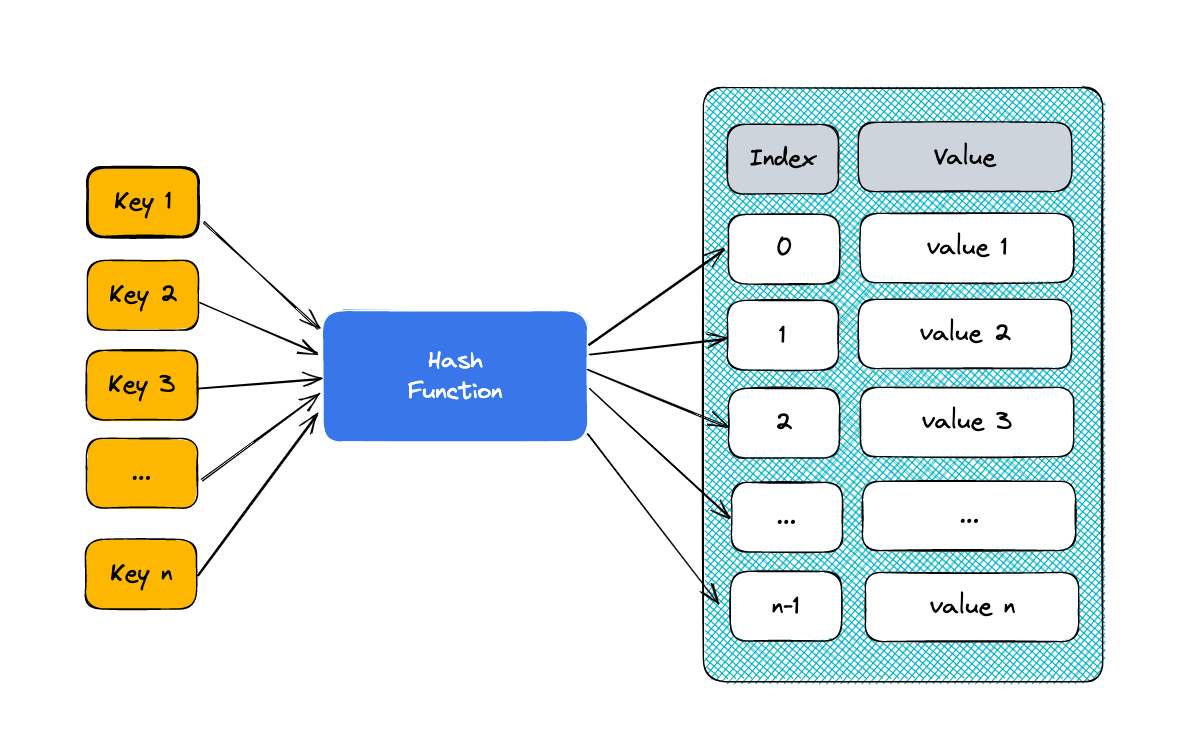
A hash table is a data structure that allows you to store and retrieve values associated with a specific key in an efficient manner. It uses a hash function to compute an index into an array of buckets or slots, from which the desired value can be found.
Here’s how it works:
-
Hash Function: When you want to store data in a hash table, a hash function is applied to the key. The hash function converts the key into an index, a numeric value that represents the position in the hash table array where the associated value will be stored.
-
Array of Buckets: The hash table consists of an array (often called a hash table array) where values are stored. Each index in the array is known as a bucket or slot.
-
Collisions: Since hash functions can produce the same index for different keys (a situation known as a collision), hash tables must have a strategy for handling these collisions. Common techniques include chaining (where each bucket contains a linked list of key-value pairs) and open addressing (where the hash table searches for the next open slot in the array).
-
Efficient Operations: Hash tables provide fast insertion, deletion, and lookup operations. When you want to find a value associated with a specific key, the hash function calculates the index, and then the hash table quickly retrieves the value from the corresponding bucket. The time complexity for these operations is often considered to be O(1) on average, making hash tables very efficient for handling large datasets.
Hash tables are widely used in various applications such as databases, caches, symbol tables in compilers, and in many other scenarios where fast data retrieval based on a key is required. The efficiency of hash tables largely depends on the quality of the hash function and the method used to handle collisions.