Jump search
Jump Search is an algorithm designed for sorted arrays. It is a block-based search algorithm that works by jumping ahead by fixed steps and then linearly searching within the block for the target element. The algorithm combines the efficiency of binary search with the simplicity of linear search.
How it work:
Step 1: Determine the jump size by taking the square root of the array length. This ensures a balanced trade-off between the number of jumps and the linear search within a block.
Step 2: Start at the beginning of the array and move ahead by the calculated jump size until finding a value that is greater than or equal to the target.
Step 3: Perform a linear search within the block from the previous jump until finding the target element or checking that it is not there.
Step 4: Repeat the process until the entire array is searched or the target element is found.
Key Characteristics:
Sorted Array: Jump search requires the array to be sorted in ascending order. This is required characteristic.
Block Jumping: The algorithm works by jumping ahead by fixed steps (often referred to as block size or jump size) instead of dividing the search space in half at each step like binary search.
Optimal Jump Size: The optimal jump size is usually calculated as the square root of the length of the array. This ensures a balance between the number of moves and the amount of comparisons needed.
Linear Search Within Blocks: After jumping to a particular block, the algorithm performs a linear search within that block.
Requires Random Access: Jump search requires random access to elements in the array. This means it is more suitable for data structures like arrays or lists.
Adaptive: The algorithm can be adapted to different scenarios by adjusting the jump size. Smaller jump sizes can reduce the number of comparisons but increase the number of jumps, while larger jump sizes have the opposite effect.
Not Recursive: Unlike binary search, jump search is typically implemented iteratively rather than recursively.
Suitable for Large Arrays: The algorithm is particularly suitable for large arrays due to more efficient work with memory.
Balances Efficiency and Simplicity: Jump search strikes a balance between the simplicity of linear search and the efficiency of binary search, making it a practical choice in scenarios where a trade-off between simplicity and efficiency is acceptable.
Space Complexity: Jump search has a space complexity of O(1), meaning it requires only a constant amount of additional space.
Applications: The algorithm can be useful in scenarios where binary search is not suitable due to memory constraints or when the dataset is relatively large and needs a more efficient search than linear search.
Applications:
Search in Databases: Jump search can be applied in databases to search for records based on certain criteria, especially when the data is stored in sorted arrays or tables.
File Systems: In file systems, the algorithm can be utilized to locate files within directories or to search for specific content within files.
Web Indexing: Jump search can be employed in web indexing algorithms to search for keywords within web pages or documents.
Data Compression Algorithms: The algorithm can be used in data compression ones to quickly locate patterns or repeated sequences within data streams.
Sparse Arrays: Jump search is effective for searching in sparse arrays where there are large gaps between elements. It helps to decrease the number of unnecessary comparisons.
Database Indexing: The algorithm can be utilized in database indexing structures, such as B-trees or skip lists, to quickly locate entries within the index. It provides a fast method for searching within indexed structures.
Text Editors and Word Processors: Jump search can be used into text editors or word processors to implement features like find word or bunch of phrase.
Genetic Sequence Analysis: In bioinformatics, the algorithm can be applied to efficiently search for specific patterns or sequences within genetic data. It helps analyze DNA or protein sequences in large datasets.
Network Routing: Jump search can be used in network routing algorithms to efficiently search for routes or paths between network nodes. It helps to find an optimal route while minimizing the number of hops or comparisons.
Data Mining: The algorithm can be employed in data mining tasks to search for patterns or anomalies within large datasets. It helps in quickly identify relevant data points or clusters.
Time Complexity:
The time complexity of Jump Search is -add formula-,, where-add formula-, is the size of the array. This makes it efficient for large datasets when compared to linear search but may be outperformed by binary search for certain scenarios.
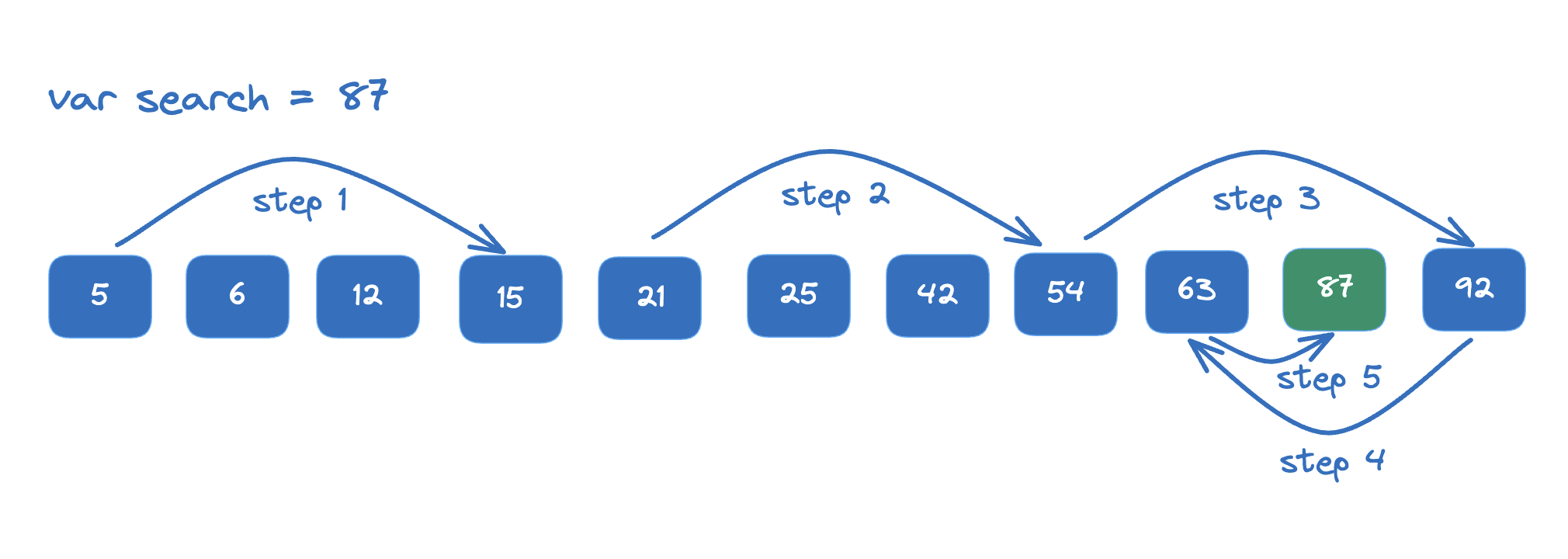
Example:
function jumpSearch(arr: number[], target: number): number {
const n = arr.length;
const step = Math.floor(Math.sqrt(n));
let prev = 0;
while (arr[Math.min(step, n) - 1] < target) {
prev = step;
step += Math.floor(Math.sqrt(n));
if (prev >= n) {
return -1;
}
}
for (let i = prev; i < Math.min(step, n); i++) {
if (arr[i] === target) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}