Floyd-Warshall algorithm
The Floyd-Warshall Algorithm is a dynamic programming algorithm used to find the shortest paths between all pairs of vertices in a weighted graph. Unlike Dijkstra’s algorithm and Bellman-Ford one, Floyd-Warshall works with graphs that can have both positive and negative edge weights and can handle graphs with cycles. The algorithm iteratively updates the shortest path distances between all pairs until reaching the optimal solution.
How it works:
Step 1: Create a matrix to represent the distances between all pairs of vertices. Initialize it with the direct edge weights and set the distances to infinity where there is no direct edge. Define the diagonal of the matrix to zeros since the distance from a vertex to itself is zero.
Step 2: For each vertex ‘k’, iterate through all pairs of vertices ‘i’ and ‘j’. Check if the path from ‘i’ to ‘j’ through ‘k’ is shorter than the current known path from ‘i’ to ‘j’. If yes, update the distance from ‘i’ to ‘j’ with the shorter path.
Step 3: Repeat the process for all vertices as intermediate ones (‘k’). After each iteration, the matrix reflects the shortest distances between all pairs of vertices considering all possible intermediate vertices.
Step 4: The final matrix contains the shortest distances between all pairs of vertices.
Key Characteristics:
All-pairs shortest path: Unlike Dijkstra’s algorithm, which finds the shortest paths from a single source vertex to all other vertices, Floyd-Warshall finds the shortest paths between all pairs of vertices in a weighted graph.
Dynamic programming approach: The algorithm uses a dynamic programming approach to solve the problem. It iteratively builds up solutions to subproblems, which are then used to solve larger subproblems until the entire problem is solved.
Space complexity: The space complexity of the algorithm is O(V^2), where V is the number of vertices in the graph. This is because the algorithm requires a matrix to store the shortest distances between all pairs of vertices.
Handling negative edge weights: Unlike Dijkstra’s algorithm, the Floyd-Warshall one can handle graphs with negative edge weights, as long as there are no negative cycles. However, if there are negative cycles, the algorithm can’t produce correct results, as there would be no shortest path in such cases.
Matrix representation: The algorithm typically uses a matrix to represent the graph and compute the shortest paths. The matrix contains the distances between all pairs of vertices, with initial values being the weights of the edges if they exist and infinity otherwise.
Intermediate vertices: In each iteration of the algorithm, it considers all vertices as potential intermediate ones in the shortest path between any pair of them. It updates the shortest distances between vertices based on whether using the intermediate vertex reduces the path length.
Path reconstruction: While the primary purpose of the Floyd-Warshall algorithm is to compute the shortest paths between all pairs of vertices, it can also be modified to reconstruct the actual paths if required, by storing additional information during the execution of the algorithm.
Applications:
Routing algorithms: In computer networking, the Floyd-Warshall algorithm can be used in routing protocols to compute shortest paths between all pairs of nodes in a network. It helps in finding the optimal paths for data packets to traverse from a source to a destination through intermediate nodes.
Traffic management: Transportation networks, such as road or rail networks, can utilize the Floyd-Warshall algorithm to optimize traffic flow by determining the shortest paths between all pairs of locations. This helps in minimizing travel time and congestion.
Flight scheduling: Airlines use the Floyd-Warshall algorithm to optimize flight routes and schedules by computing the shortest paths between airports. This ensures efficient utilization of resources and minimizes flight delays.
Geographic information systems (GIS): GIS applications use the Floyd-Warshall algorithm for route planning, navigation, and network analysis. It helps in finding the shortest paths between different geographic locations considering various factors such as terrain, road conditions, and traffic.
Robotics and autonomous vehicles: In robotics and autonomous vehicle navigation, the Floyd-Warshall algorithm can be employed to plan optimal paths for robots or vehicles to navigate in complex environments while avoiding obstacles and reaching their destinations efficiently.
Telecommunication networks: Telecommunication networks, including telephone and data networks, use the Floyd-Warshall algorithm to optimize communication paths between all pairs of nodes. This ensures efficient data transmission and minimizes network congestion.
Social network analysis: In social network analysis, the Floyd-Warshall algorithm can be applied to model relationships between individuals or entities in a network. It helps in identifying the shortest paths between users, analyzing network connectivity, and studying information diffusion processes.
Game development: The Floyd-Warshall algorithm can be used in game development for pathfinding in game environments. It helps in determining the shortest paths for characters or objects to navigate through obstacles in a game world.
Time Complexity:**
The time complexity of Floyd-Warshall Algorithm is (O(V^3)), where (V) is the number of vertices in the graph.
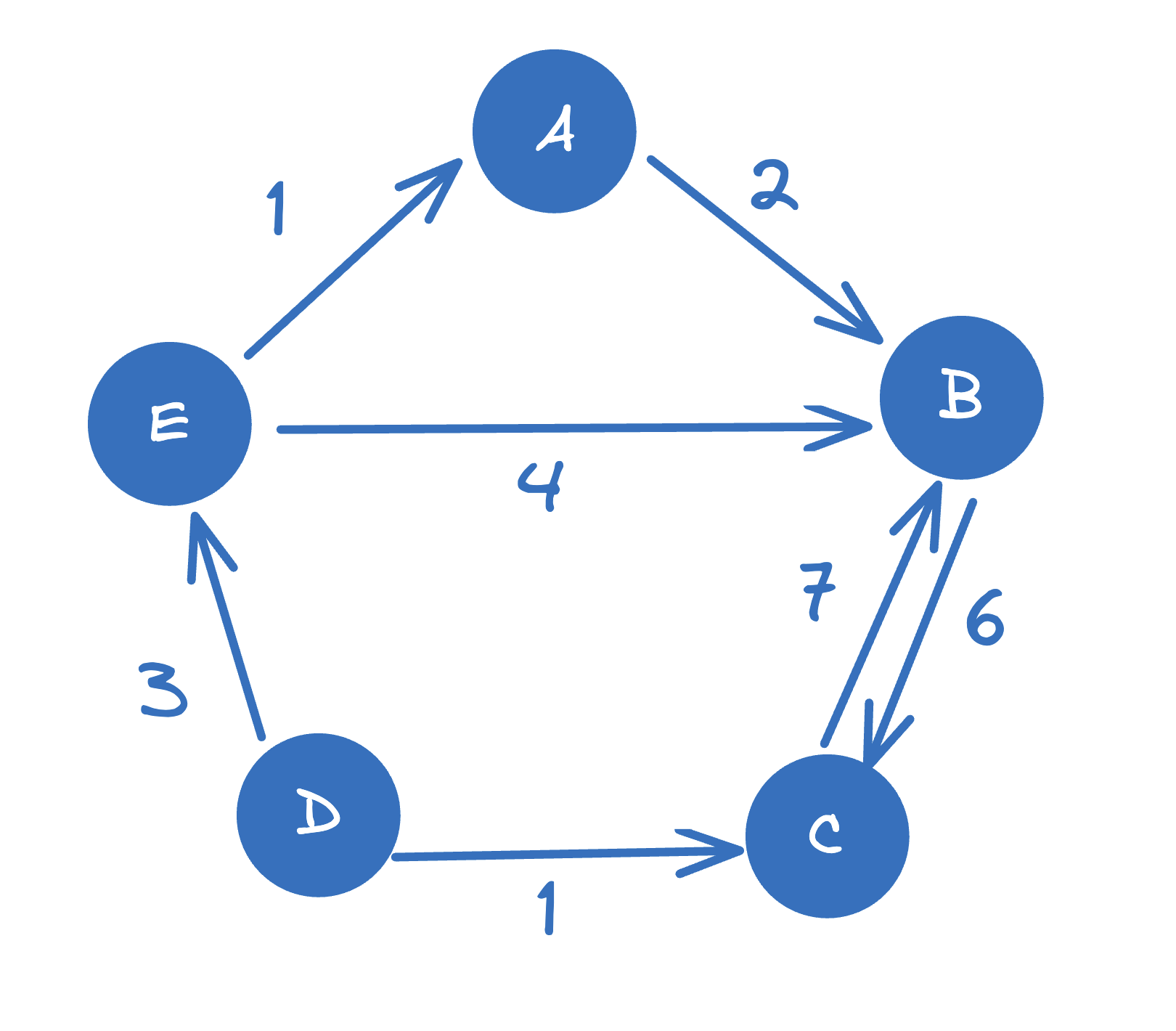
Example:
class Graph {
private adjacencyMatrix: number[][];
constructor(numVertices: number) {
this.adjacencyMatrix = Array.from({ length: numVertices }, () =>
Array(numVertices).fill(Infinity)
);
// Set diagonal elements to 0
for (let i = 0; i < numVertices; i++) {
this.adjacencyMatrix[i][i] = 0;
}
}
addEdge(source: number, destination: number, weight: number) {
this.adjacencyMatrix[source][destination] = weight;
}
floydWarshall() {
const numVertices = this.adjacencyMatrix.length;
for (let k = 0; k < numVertices; k++) {
for (let i = 0; i < numVertices; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < numVertices; j++) {
if (
this.adjacencyMatrix[i][k] + this.adjacencyMatrix[k][j] <
this.adjacencyMatrix[i][j]
) {
this.adjacencyMatrix[i][j] =
this.adjacencyMatrix[i][k] + this.adjacencyMatrix[k][j];
}
}
}
}
return this.adjacencyMatrix;
}
}
// Example usage:
const graph = new Graph(4);
graph.addEdge(0, 1, 3);
graph.addEdge(0, 2, 6);
graph.addEdge(1, 2, 1);
graph.addEdge(1, 3, 4);
graph.addEdge(2, 3, 2);
const result = graph.floydWarshall();
console.log("Shortest Path Matrix:");
for (const row of result) {
console.log(row);
}