Breadth First search
Breadth-First Search (BFS) is a graph traversal algorithm that systematically explores all the vertices of a graph in breadthward motion, level by level. It starts at a chosen vertex and visits all its neighbors before moving on to other ones. BFS is commonly used to find the shortest path in an unweighted graph and to explore the structure of a graph.
How it works:
Step 1: Initialize queue and begin by selecting a starting vertex and enqueue it into a queue.
Step 2: Dequeue a vertex from the front of the queue and explore all its neighbors. Enqueue any unvisited ones, marking them as visited to avoid duplication.
Step 3: Continue the process level by level, exploring all vertices at the current one before moving on to the next level.
Step 4: Repeat until the queue is empty, ensuring that all reachable vertices are visited.
Key Characteristics:
Queue-Based: BFS utilizes a queue data structure to keep track of the nodes that need to be visited.
Level Order Traversal: BFS systematically explores all nodes at the current level before moving on to the next one. This ensures that nodes are visited in increasing order of their distance from the starting node.
Non-Recursive (typically): While BFS can be implemented recursively, it is typically implemented iteratively using a queue due to better space efficiency and avoidance of potential stack overflow issues, especially for large graphs.
Complete (for finite graphs): The algorithm will visit all nodes reachable from the starting node in a finite graph. However, for infinite or cycled graphs, proper termination conditions need to be implemented to avoid infinite loops.
Optimal for Shortest Path (unweighted graphs): BFS is optimal for finding the shortest path between two nodes in an unweighted graph. This is because BFS guarantees that the first occurrence of a node during traversal will result in the shortest path to that node.
Memory Consumption: The algorithm typically requires more memory compared to Depth First Search (DFS) as it needs to store all the nodes at the current level in the queue. However, in practice, BFS can be more memory-efficient for very deep graphs because it does not suffer from the recursion depth limitations of DFS.
Traversal from Source Node: BFS starts traversal from a source node and explores all its adjacent ones before moving on to the next level. This process continues until all reachable nodes are visited.
Applications:
Shortest Path and Minimum Spanning Tree: BFS can be used to find the shortest path between two nodes in an unweighted graph.
Web Crawling and Search Engine Indexing: BFS is used in web crawlers to systematically traverse the web graph starting from a given seed URL.
Social Network Analysis: BFS is employed to analyze social networks, where nodes represent individuals, and edges represent relationships between them.
Network Broadcasting and Routing: The algorithm can be utilized in network protocols for broadcasting messages or routing packets.
Shortest Path in a Maze: BFS is commonly used to find the shortest path from a starting point to a destination in a maze. Each cell of the maze is considered a node, and BFS explores adjacent cells level by level until the destination is reached.
Puzzle Solving: BFS is employed in puzzle-solving algorithms, such as solving sliding block puzzles (e.g., 15-puzzle), Rubik’s Cube, or Sudoku. It helps in finding the shortest sequence of moves or steps to reach the goal state.
Garbage Collection: The algorithm is used in memory management systems for garbage collection. It helps identify and mark reachable objects from the root set, ensuring that only reachable objects are retained in memory.
Process Scheduling and Resource Allocation: BFS can be applied in operating systems for process scheduling and resource allocation. It helps in scheduling processes based on their priority levels or allocating resources optimally while considering dependencies.
Routing in Networks and GPS Navigation: In networks, BFS can be used for routing packets based on the hop count, ensuring efficient data transmission. In GPS navigation systems, BFS assists in finding the shortest route between two locations on a map.
Game AI and Pathfinding: BFS is utilized in game development for pathfinding algorithms to navigate characters or units in a game environment. It helps in finding optimal paths while avoiding obstacles or enemies.
Time Complexity:
The time complexity of BFS is (O(V + E)), where (V) is the number of vertices and (E) is the number of edges. The algorithm visits each vertex and edge once.
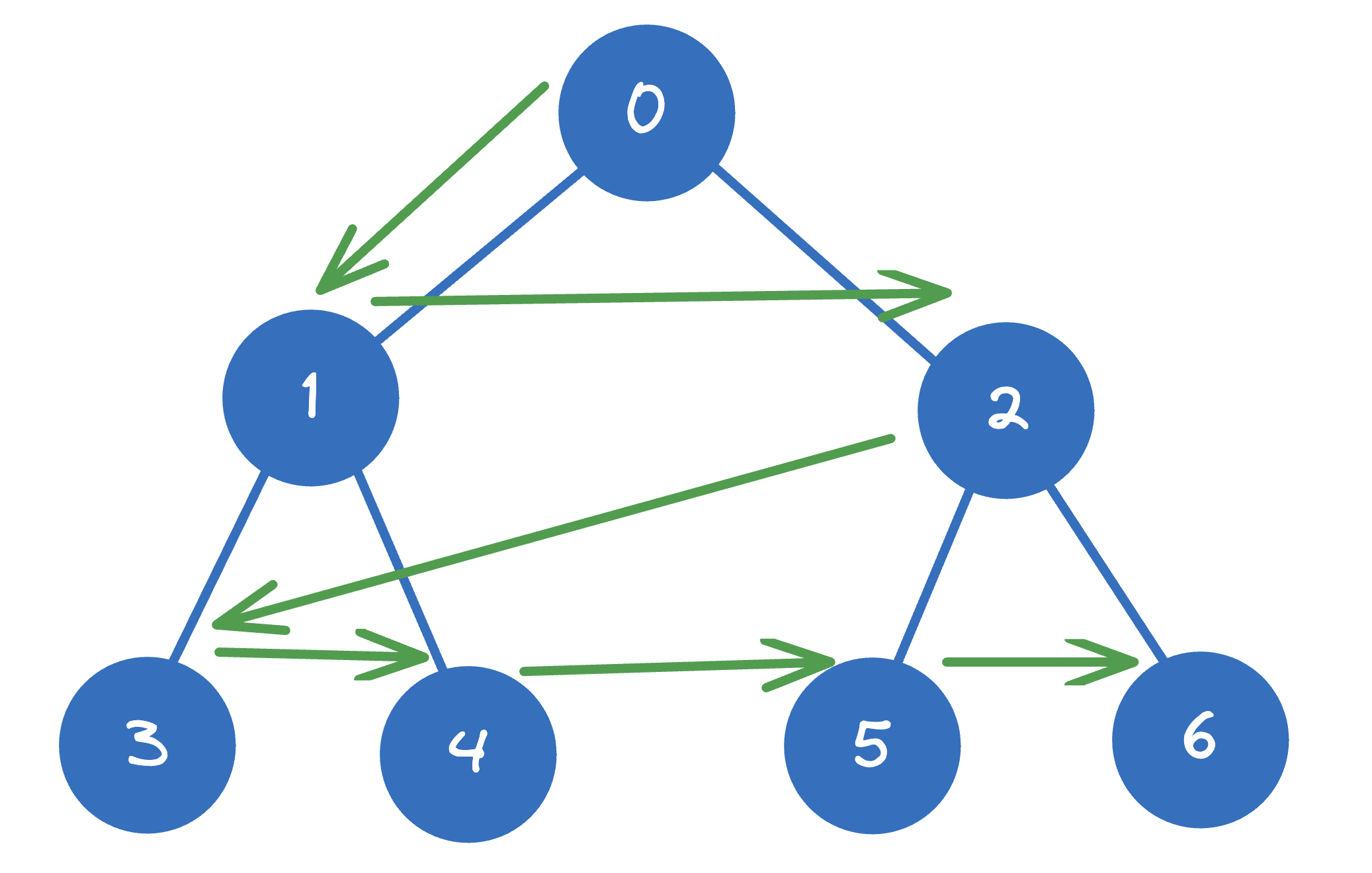
Example:
class Graph {
private adjacencyList: Map<string, string[]>;
constructor() {
this.adjacencyList = new Map();
}
addVertex(vertex: string) {
if (!this.adjacencyList.has(vertex)) {
this.adjacencyList.set(vertex, []);
}
}
addEdge(vertex1: string, vertex2: string) {
this.adjacencyList.get(vertex1)?.push(vertex2);
this.adjacencyList.get(vertex2)?.push(vertex1);
}
bfs(startingVertex: string) {
const visited: Set<string> = new Set();
const queue: string[] = [];
visited.add(startingVertex);
queue.push(startingVertex);
while (queue.length > 0) {
const currentVertex = queue.shift()!;
console.log(currentVertex);
const neighbors = this.adjacencyList.get(currentVertex) || [];
for (const neighbor of neighbors) {
if (!visited.has(neighbor)) {
visited.add(neighbor);
queue.push(neighbor);
}
}
}
}
}
// Example usage:
const graph = new Graph();
graph.addVertex("A");
graph.addVertex("B");
graph.addVertex("C");
graph.addVertex("D");
graph.addEdge("A", "B");
graph.addEdge("A", "C");
graph.addEdge("B", "D");
graph.bfs("A");