Binary search
Binary Search is defined as a searching algorithm used in a sorted array by repeatedly dividing the search interval in half. The idea of binary search is to use the information that the array is sorted,.
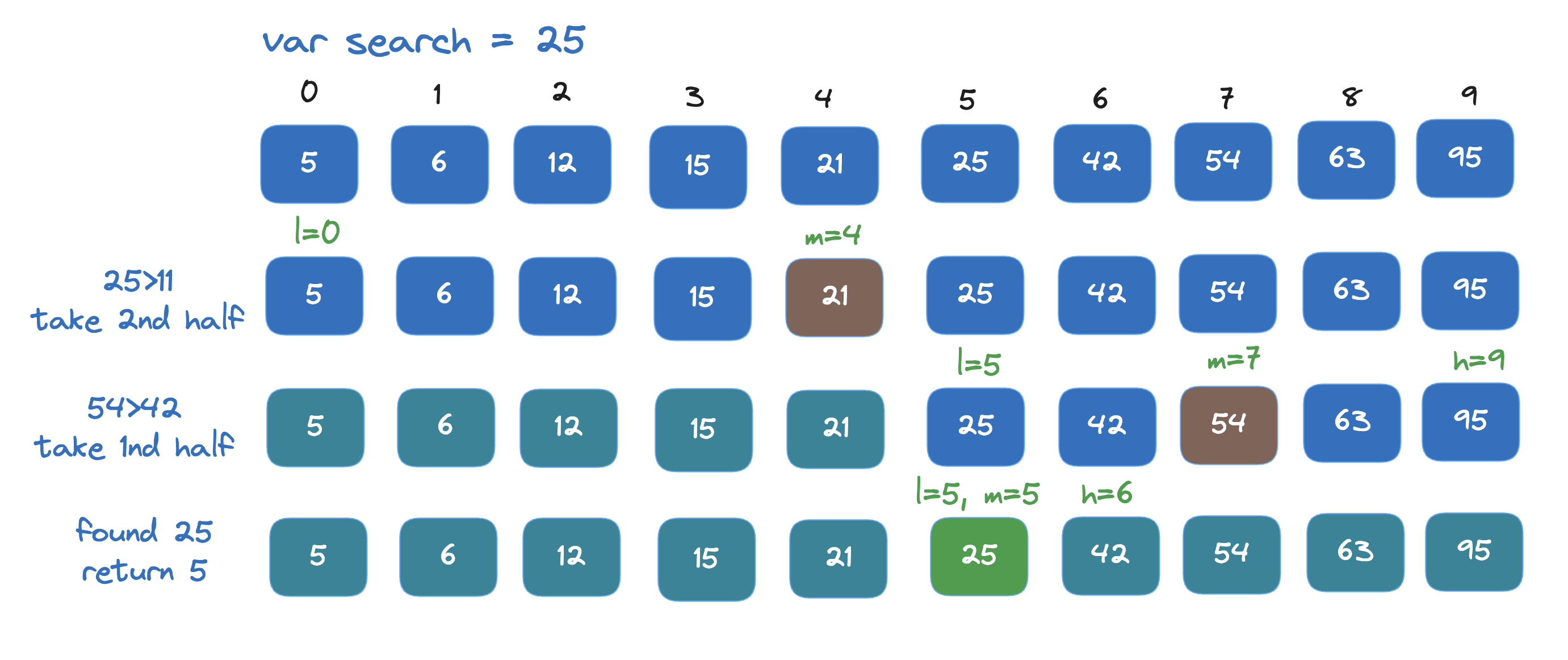
How it works:
Step 1: Start with a sorted array and a target value.
Step 2: Set the left and right pointers to the start and end of the array.
Step 3: Calculate the middle index and compare the middle element with the target.
Step 4: Adjust the search interval based on the comparison.
Step 5: Repeat until the target is found or the search interval is empty.
Key Characteristics:
Divide and Conquer Approach: Binary search follows the principle of “divide and conquer.” It repeatedly separate the search interval in half until the target element is found or the interval is empty.
Efficiency: This algorithm is highly efficient, particularly for large datasets, because it eliminates half of the remaining elements in each step. It has a time complexity of O(log n), where n is the number of elements in the array.
Requirement of Sorted Data: Binary search requires the data to be sorted beforehand. This ensures that the algorithm can reliably make decisions about which half of the array to search in.
Iterative or Recursive Implementation: Binary search can be implemented either iteratively or recursively. Both approaches follow the same logic but differ in their implementation details.
Midpoint Calculation: In each iteration, the algorithm calculates the midpoint of the search interval to determine whether the target element lies in the left or right half of the interval.
Termination Condition: Binary search terminates when the search interval is empty, indicating that the target element is not present in the array, or when the target element is found.
Space Complexity: The algorithm has a space complexity of O(1), meaning it requires constant extra space for storing variables regardless of the size of the input array.
Works on Random Access Data Structures: Binary search is ideal for arrays or other data structures that allow random access to elements, such as arrays or certain types of lists.
Applications:
Searching in Databases: Binary search is widely used in databases for fast retrieval of records based on keys. Databases often use sorted indexes to enable binary search, which significantly reduces the time required to locate specific records.
Searching in Trees and Graphs: The algorithm is employed in various tree-based and graph-based data structures like binary search trees, AVL trees, and red-black trees for efficient searching and retrieval of elements.
Sorting Algorithms: Binary search is utilized in sorting algorithms such as quicksort and mergesort to efficiently partition and merge elements. Although these sorting algorithms primarily rely on divide-and-conquer techniques, binary search plays a crucial role in the process.
Finding Median and Percentile: The algorithm is used to find the median or percentile in a sorted array or list. By repeatedly narrowing down the search range, binary search efficiently locates the desired element, providing quick statistical analysis capabilities.
Searching in Texts: Binary search can be applied in text processing applications for tasks such as searching for keywords or phrases in sorted text files or dictionaries. This is particularly useful in applications like spell checkers or autocomplete features.
Network Routing: The algorithm is utilized in network routing algorithms to efficiently locate routes in routing tables. By organizing routing information in sorted structures, binary search can quickly identify the optimal path for data packets in computer networks.
Approximate Matching and Fuzzy Searching: Binary search can be adapted for approximate matching or fuzzy searching applications where exact matches are not required. By defining appropriate search criteria and tolerances, binary search can efficiently locate approximate matches in sorted datasets.
Genetics and Bioinformatics: Binary search is used in various bioinformatics applications for tasks such as searching for specific DNA sequences or analyzing genomic data. Its efficiency makes it valuable for processing large volumes of genetic information.
Game Development: Binary search is employed in various game development scenarios, such as pathfinding algorithms or determining optimal strategies. For example, in certain types of games, binary search can be used to efficiently locate targets or identify the best course of action.
Resource Allocation: Binary search can be applied in resource allocation problems, such as scheduling tasks or managing inventory. By efficiently searching for available resources or optimal scheduling slots, binary search helps optimize resource utilization and allocation.
Time Complexity:
- Worst case: O(log n)
- Average case: O(log n)
- Best case: O(1)
Example:
function binarySearch(nums: number[], target: number): number {
let left: number = 0;
let right: number = nums.length - 1;
while (left <= right) {
const mid: number = Math.floor((left + right) / 2);
if (nums[mid] === target) return mid;
if (target < nums[mid]) right = mid - 1;
else left = mid + 1;
}
return -1;
}
class Solution {
private static int binarySearch(int[] array, int target) {
int low = 0;
int high = array.length - 1;
while(low <= high) {
int middle = low + (high - low) / 2;
int value = array[middle];
if(value < target) {
low = middle + 1;
} else if(value > target) {
high = middle - 1;
} else {
return middle;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
def binary_search(list, item):
low = 0
high = len(list) - 1
while low <= high:
mid = (low+high)/2
guess = list[mid]
if guess == item:
return mid
if guess > item:
high = mid - 1
else:
low = mid +1
return None
my_list = [1, 3, 5, 7, 9]
res = binary_search(my_list, 3)
print(my_list[res])